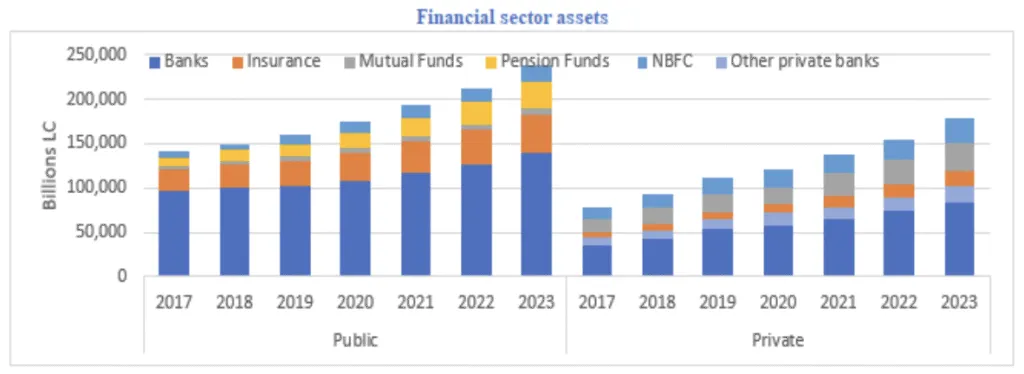
India’s financial sector is large and well-developed, with total financial assets equal to about 187% of the country’s GDP. The banking system is the main part of this sector and includes Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), and Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs). Together, these banks make up around 56% of all financial sector assets.
Bank Lending Focuses on Productive Sectors
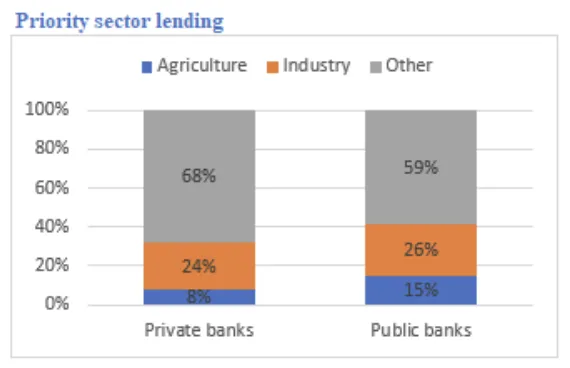
Most bank lending in India is used for productive activities, especially short- and medium-term loans. These loans are mainly funded through retail deposits. As of March 2024:
- Retail loans made up about one-third of total bank credit.
- Housing loans formed about half of all retail loans.
- The other two-thirds of lending went to services, industry, and agriculture.
- About 75% of bank loans are secured, which reduces risk for banks.
Deposits Are the Main Funding Source
Bank deposits continue to be the most important source of funds for Indian banks.
- Total deposits equal 73% of GDP, similar to other countries at India’s level of development.
- Deposits form 78% of all bank loans.
- Nearly 65% of deposits mature within three years, matching the duration of most bank loans.
NBFCs Are Growing but Depend on Wholesale Funding
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) also play a major role in lending. Retail loans form about one-third of their lending as well. However, unlike banks, NBFCs depend mainly on wholesale funding. Deposits make up only 2% of their total liabilities.
Role of State-Owned Financial Institutions Is Declining
State-Owned Financial Institutions (SOFIs)—such as Public Sector Banks (PSBs), public insurers, RRBs, and development banks—still hold a large share of financial assets, though their role is slowly reducing.
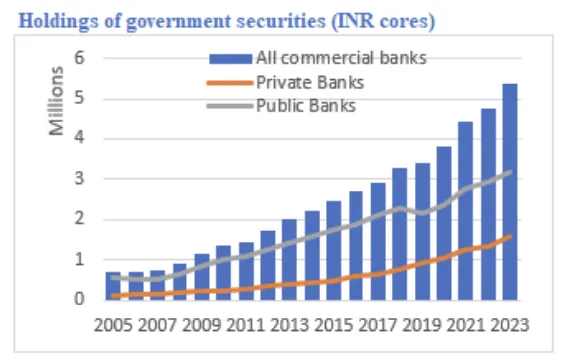
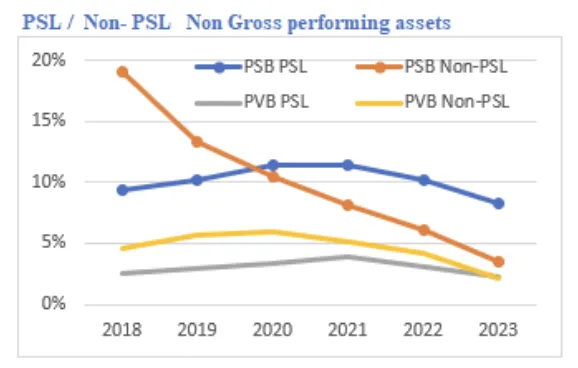
In 2023, SOFIs held 55% of financial sector assets, down from 63% in 2017. This decline is due to a lower share of PSBs and public insurers. PSB credit growth has been slower than that of private banks in recent years. Despite consolidation, government ownership in the banking sector remains high.
RRBs, development banks, and government programs continue to support underserved groups such as MSMEs, rural populations, and infrastructure projects.