Ethiopia Volcano Eruption: Severe Health Impact on India, DGCA issues advisory to Airlines
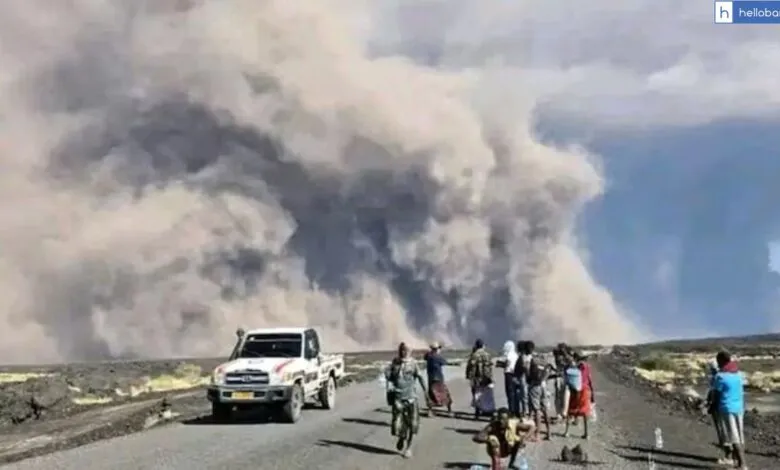

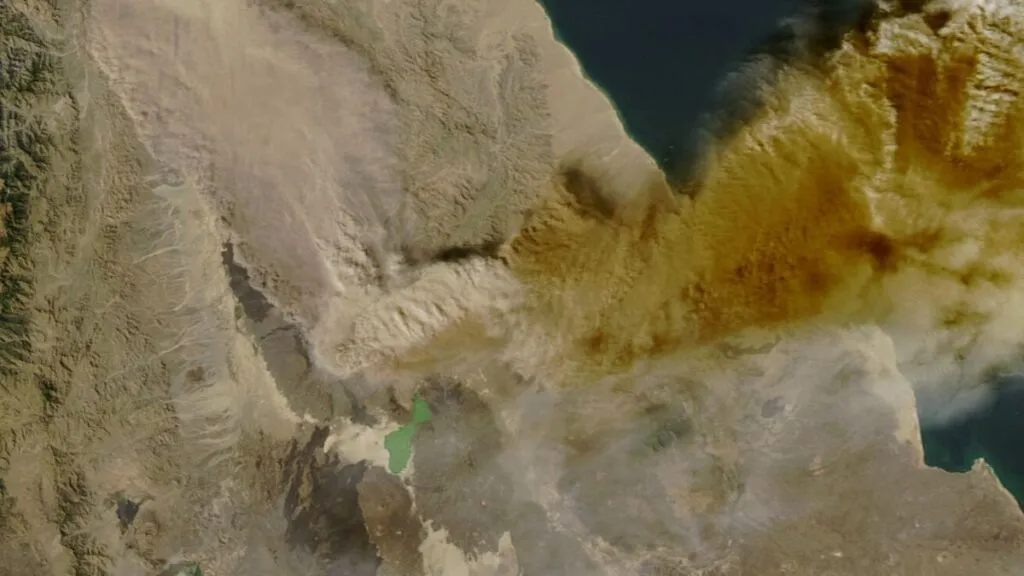
Ethiopia Volcano Eruption: The Hayli Gubbi volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar region erupted on Sunday for the first time in nearly 12,000 years. This led to thick ash plumes across the Red Sea toward Yemen and Oman. The cloud has now extended over the northern Arabian Sea. This has led to health scares in parts of India. The long-dormant Hayli Gubbi volcano in the Afar region of Ethiopia erupted over the weekend, sending ash plumes up to 14 km high. The volcanic ash crossed the Red Sea toward Yemen and Oman and then travelled to parts of Pakistan and northern India. The ash cloud is moving towards China and is expected to leave Indian skies by 1400 GMT (7:30 PM IST) Tuesday (November 25).

Ethiopia is the second most populous nation in Africa after Nigeria.
The ash cloud entered India late on Monday, raising fears of its impact on human health and air quality. India’s aviation regulator, the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), also issued an advisory yesterday to all airlines to avoid areas affected by the volcanic ash.
According to environmentalist Vimlendu Jha, ash from Ethiopia’s volcano is now “floating around” over Indian regions like Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Delhi. While the sulphur dioxide and glass particle clouds are enormous, Jha reassured that because the ash remains in the “very upper atmosphere,” its impact will not immediately affect Delhi’s AQI, though he advised continued monitoring.
The latest analysis by India Met Sky Weather confirms the ash plume, which had previously caused flight disruptions in India, has moved away from Northern India and is dispersing into the upper atmosphere over China and the Pacific.
What is volcanic ash?
Volcanic ash is a very fine powder of tiny rock fragments, minerals, and volcanic glass that is thrown into the air during a volcanic eruption. Volcanic ash is made of hard, sharp particles. The ash cloud is moving at speeds of up to 100-120 km/h over North India at altitudes between 15,000-45,000 feet. According to IndiaMetSky Weather, the ash from the volcanic eruption in Ethiopia is made up of sulphur dioxide, glass and fine rock particles.
Meteorological agencies reported that the ash cloud entered India via western Gujarat and then crossed into Rajasthan, north-west Maharashtra, Delhi, Haryana, and Punjab by late Monday.
Why is Volcanic Ash Harmful?
Volcanic eruptions can affect human health in several ways, mainly because they release ash, gases, heat and debris into the environment. The most common health problem comes from breathing volcanic ash, which contains tiny, sharp particles of rock and glass. When inhaled, these particles can irritate the nose, throat and lungs, leading to coughing, sore throat, wheezing, asthma attacks and bronchitis. People who already have breathing problems, young children, the elderly and those with chronic lung diseases are at higher risk.
Volcanic ash can also irritate the eyes. The fine particles can cause redness, watering, itching and a burning sensation. In some cases, if ash gets into the eyes repeatedly, it can even scratch the surface of the eye. Skin irritation is another concern, as ash can cause rashes, itching and dryness, especially in sensitive individuals.
Volcanoes release several gases, such as sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide. These gases can cause chest tightness, breathing difficulty, headaches and eye irritation. Exposure to high concentrations of these gases can be dangerous and, in rare cases, fatal—especially in low-lying areas where gases can accumulate.
People living close to the eruption may also suffer burns or injuries from lava, hot ash flows, falling rocks or collapsing structures. In addition, volcanic ash can contaminate drinking water and food, leading to stomach problems if consumed. Beyond physical health, volcanic eruptions can also affect mental well-being. Experiencing an eruption or living in an affected area can lead to stress, anxiety, fear and sleep disturbances.
Long-term exposure to volcanic ash is uncommon but can lead to chronic respiratory issues, particularly in cleanup workers or people who are constantly exposed to large amounts of ash. Overall, volcanic eruptions affect health through inhalation of ash and toxic gases, physical injuries, contaminated resources and psychological stress.
How can Volcanic Ash impact Airlines?
Volcanic ash can severely affect flights because it is made of tiny, sharp particles of rock and glass that can damage aircraft systems. When a plane flies through an ash cloud, the ash can be sucked into the engines. Inside the engine’s extremely high temperatures, the ash can melt and then solidify again on cooler parts, which can block airflow and cause the engine to fail. In several past incidents, planes temporarily lost all engine power after flying through volcanic ash clouds.
Ash also affects visibility. It can make the sky look hazy or dark, making it harder for pilots to see. The particles can scratch the cockpit windows, reducing clarity and making navigation difficult. Volcanic ash can also damage the exterior of the aircraft, scratch the body and wings, and block sensors that help in flight operations, such as speed and altitude indicators.
In addition, ash clouds are not always detected on normal weather radar, which makes them dangerous because pilots may not realize they are entering an ash-filled area. This is why aviation authorities often close airspace near erupting volcanoes and reroute flights to prevent planes from accidentally flying into ash clouds.
Overall, volcanic ash poses a serious threat to aircraft by damaging engines, reducing visibility, interfering with navigation systems and affecting the safety of the flight.
