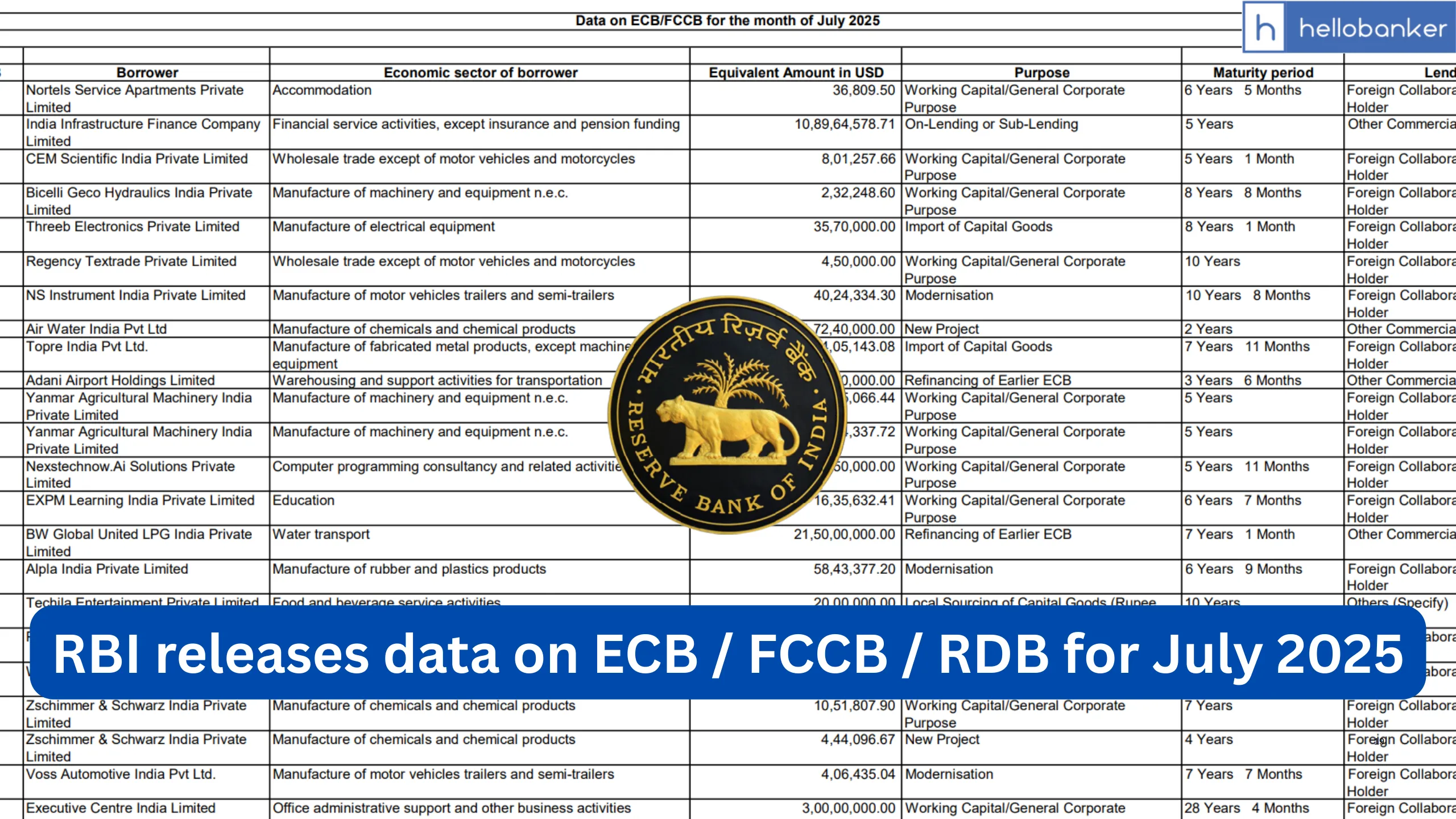
The Reserve Bank of India has today released the data on External Commercial Borrowings (ECB), Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCB) and Rupee Denominated Bonds (RDB) both, through Automatic Route and Approval Route, for the month of July 2025. First let’s understand what is ECB, FCCB and RDB. After that you can download data from link given at last.
1. External Commercial Borrowings (ECB)
- These are loans taken by Indian companies from foreign lenders (like banks, financial institutions, or other investors) in foreign currency.
- Example: An Indian company borrowing USD 100 million from a Japanese bank.
- Purpose: To fund expansion, infrastructure projects, or other business needs.
- Advantage: Access to large funds at international interest rates, often lower than domestic rates.
- Risk: Repayment has to be made in foreign currency → if the rupee weakens, repayment becomes costlier.
2. Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCB)
- These are special types of bonds issued by Indian companies in foreign currency.
- Investors buy them and earn interest. Later, they have the option to convert these bonds into equity shares of the company at a pre-decided price.
- Example: An Indian company issues FCCBs worth USD 50 million → foreign investors can either redeem in cash or convert into shares of the company.
- Advantage: If the company does well, investors convert bonds into shares and benefit from share price appreciation.
- Risk: If share price falls, investors may not convert, and the company still has to repay the debt.
3. Rupee Denominated Bonds (RDB) / Masala Bonds
- These are bonds issued by Indian companies in international markets but denominated in Indian Rupees (not in foreign currency).
- Example: An Indian company issues bonds worth ₹500 crore in London market. Foreign investors buy them, but repayment is in rupees.
- Advantage: Currency risk is borne by the investor, not the Indian company (unlike ECBs).
- Also helps bring foreign investment into India.
| Feature | ECB (External Commercial Borrowings) | FCCB (Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds) | RDB (Rupee Denominated Bonds / Masala Bonds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Currency of Issue | Foreign currency (e.g., USD, JPY, EUR) | Foreign currency (e.g., USD) | Indian Rupees (₹) |
| Who Lends/Invests | Foreign banks, institutions, investors | Foreign investors | Foreign investors |
| Repayment | In foreign currency | In foreign currency (or converted into equity shares) | In Indian Rupees |
| Conversion Option | Not applicable | Can be converted into equity shares of issuing company | Not convertible into equity |
| Risk of Currency Fluctuation | Borrower bears the risk | Borrower bears the risk (unless converted to equity) | Investor bears the risk |
| Use/Purpose | Loans for expansion, infrastructure, working capital | Raising funds with option to dilute equity later | Raising funds from global markets without forex repayment risk |
| Example | An Indian company borrows USD 100m from a Japanese bank | Indian company issues USD 50m FCCBs that can later turn into shares | Indian company issues ₹500 cr. Masala Bonds in London market |